The NEC MC-SNICS (Multi-Cathode Source of Negative Ions by Cesium Sputtering) is most commonly used in Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) systems to generate negative ions. Contact us to learn more.
NEC manufactures negative ion sources for a variety of applications. The Multi-Cathode Source of Negative Ions by Cesium Sputtering (MC-SNICS) was originally developed as a reliable sputter source for applications that required rapid cathode change and precise, repeatable positioning without cathode exposure to air. This source is most commonly used in AMS systems for the production of beams such as C, Be, I, Ca, Cl, and the actinides. Like the SNICS, it can create ion beams from all elements that form a stable negative ion.
The MC-SNICS principle of operation is very similar to the single cathode SNICS source, with the exception of using a spherical ionizer instead of a conically shaped ionizer. Here’s how it works.
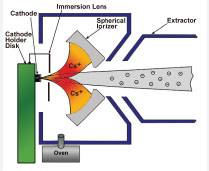
The MC-SNICS uses the basic elements from the SNICS II ion source, with the addition of cathode indexing system that allows the change of cathodes without breaking vacuum. The indexing system features:
There are two models of the MC-SNICS:
Though the MC-SNICS source is primarily designed for the use of solid samples, NEC offers a gas option that allows the input of carbon dioxide behind a hollow titanium cathode assembly. This is available for both the 40 MC-SNICS and 134 MC-SNICS models.
A typical MC-SNICS system includes:
NEC can provide just the source, a complete injector system, or anything in-between. Contact NEC for more information on MC-SNICS injector systems.
NEC also offers manual and electric cathode presses to pack powdered elemental samples into cathodes suitable to generate negative ion beams. Contact NEC for more information.
The beam emittance is on the order of 5 πmm mR (MeV)1/2 for optimum transmission through a tandem electrostatic accelerator with proper optics.
Examples of Negative Ion Beams Produced by the MC-SNICS
Negative Ion Current after analysis Carbon >100μA Aluminum >200nA Beryllium >1.5μA Iodine ~1μA Chlorine 30μA Calcium 80nA This list is based on data from the NEC factory and contributing laboratories. All ion beam currents listed are measured after 30° or 45° mass analysis.
This is not a complete list of beams that can be produced by the MC-SNICS source. For beam current information for other elements, please contact NEC.